本笔记参考于 Agile Tutorial
H1Intro
H2What is Agile Methodology?
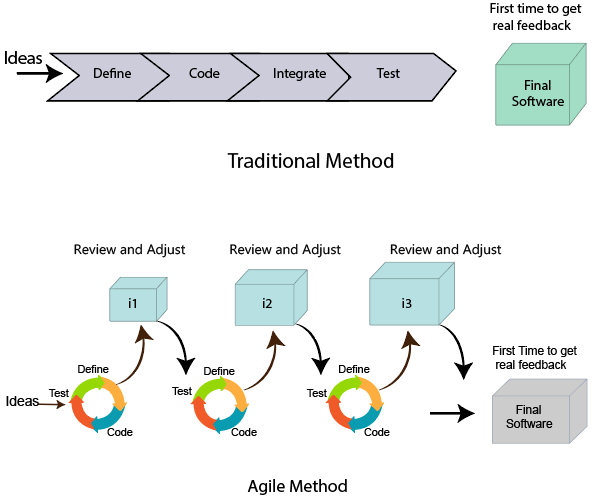
An agile methodology is an iterative approach to software development. Each iteration of agile methodology takes a short time interval of 1 to 4 weeks. The agile development process is aligned to deliver the changing business requirement. It distributes the software with faster and fewer changes.
The single-phase software development takes 6 to 18 months. In single-phase development, all the requirement gathering and risks management factors are predicted initially.
The agile software development process frequently takes the feedback of workable product. The workable product is delivered within 1 to 4 weeks of iteration.
H2Roles in Agile
H3Scrum Master
The Scrum Master is a team leader and facility provider who helps the team member to follow agile practices, so that the team member meets their commitments and customers requirements.
Responsibilities:
- They enable the close co-operation between all the roles and functions.
- They remove all the blocks which occur.
- They safeguard the team from any disturbances.
- They work with the organization to track the progress and processes of the company.
- They ensure that Agile Inspect & Adapt processes are leveraged correctly which includes
- Planned meetings
- Daily stand-ups
- Demo
- Review
- Retrospective meetings, and
- Facilitate team meetings and decision-making process.
H3Product Owner
The Product Owner is one who runs the product from a business perspective.
Responsibilities:
- He defines the requirements and prioritizes their values.
- He sets the release date and contents.
- He takes an active role in iteration and releasing planning meetings.
- He ensures that the team is working on the most valued requirement.
- He represents the voice of the customer.
- He accepts the user stories that meet the definition of done and defined acceptance criteria.
H2Cross-functional team
Every agile team contains self-sufficient team with 5 to 9 team members. The average experience of each member ranges from 6 to 10 years. The agile team contains 3 to 4 developers, 1 tester, 1 technical lead, 1 scrum master and 1 product owner.
The Scrum master and Product owner are considered as a part of Team Interface, on the other hand remaining members are the part of Technical Interface.
H2User Requirement
There may be of two type of functionality.
- As a <User Role> I want <Functionality> so that <Business Value>
- In order to <Business value> as a <User Role> I want <Functionality>.
During iteration planning, the requirement is broken down into tasks.
H3Relation between them
- User requirement talks about what is to be done. It defines the needs of users.
- Task talks about how it is to be done. It defines how functionality is implemented.
- Requirements are validated using acceptance test.
H1Advantage & Disadvantage
| Advantage | Disadvantage | |
|---|---|---|
| Agile Methodology | 1. Customer satisfaction is rapid, continuous development and delivery of useful software. 2. Daily and close cooperation between business people and developers. 3. Regular adaptation to changing circumstances. 4. Even late changes in requirements are welcomed. | 1. It is not useful for small development projects. 2. Cost is slightly more as compared to others. 3. The project can quickly go off track if the project manager is unclear about requirements and what outcome he/she wants. |
| Waterfall Model | 1. It is one of the easiest and traditional model to manage because each phase has specific deliverables and a review process. 2. It works well in smaller-size projects where requirements are easily understandable. 3. It has a faster product delivery model. 4. There are well-documented process and results. | 1. It is difficult to move back to make changes in the previous phase. 2. It is costly to fix. |
H1Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC)
Agile SDLC breaks down the product into small incremental builds. These builds are provided in iterations.
Each iteration of agile SDLC consists of cross-functional teams working on various phases:
- Requirement gathering and analysis
- Design the requirements
- Construction/ iteration
- Deployment
- Testing
- Feedback
H2Advantages of Agile SDLC
- Project is divided into short and transparent iterations.
- It has a flexible change process.
- It minimizes the risk of software development.
- Quick release of the first product version.
- The correctness of functional requirement is implemented into the development process.
- Customer can see the result and understand whether he/she is satisfied with it or not.
H2Disadvantages of Agile SDLC
- The development team should be highly professional and client-oriented.
- New requirements may be a conflict with the existing architecture.
- With further correction and change, there may be chances that the project will cross the expected time.
- It may be difficult to estimate the final cost of the project due to constant iteration.
- A defined requirement is absent.
H1Scrum
H1Kanban
Kanban is a popular framework which is used to implement agile software development. It takes real time communication of capacity and complete transparency of work. The work items are represented in a kanban board visually, allowing team members to see the state of every piece of work at any time.
H2Elements of a kanban board
These are Visual signals, columns, work-in-progress limits, a commitment point, and a delivery point.
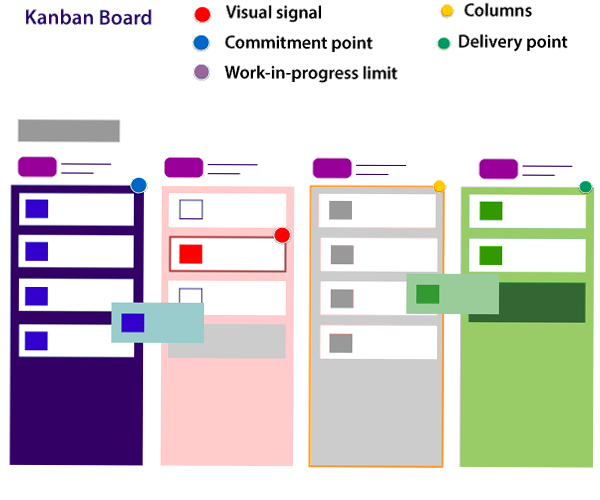
- Visual Signals: The kanban board is a visual card (stickies, tickets, or otherwise). Kanban team write their projects and work items onto cards, usually per person each card. For agile teams, each card could encapsulate into one user story. Once the board completed, this visual team helps team members and stock members quickly to understand what the team is working.
- Columns: The column represents the specific activities that compose a "workflow" together. The card flows through a workflow until its completion. The workflow may be a simple as "To Do," "In Progress," "Complete," or much more complicated.
- Work in progress (WIP) Limits: The work in progress limits are the maximum number of cards which can be in one column. This is at any given time. It gives the alert signal that you committed too much work.
- Commitment point: Kanban teams also maintain a backlog for their board. This is where the customers and team member put ideas for projects that the team can pick up. The team members pick up plans when they are ready. The committed point is a movement where the design is picked up by the team, and work starts on the project.
- Delivery point: It is the end point of a kanban team's workflow. Mostly the delivery point for every team is when the product and services are handed to the customer.
H2Kanban vs Scrum board
| Kanban | Scrum |
|---|---|
| Kanban is an ongoing process. | Scrum sprints have a start and stop dates |
| Kanban has no formal roles. | The role is clearly defined for each team in the scrum (product owner, development team, and scrum master). Both teams are self-organized. |
| A kanban board is used throughout the lifecycle of a project | Scrum board is cleared and recycled after each sprint. |
| This board is more flexible with regard to tasks and timing. Its task can be reprioritized, reassigned, or updated as needed. | This board has a number of tasks and a strict deadline to complete them. |
H1Daily Stand-up
The daily stand-up is a daily status meeting of the agile team member. This meeting roughly takes 12 to 18 minutes (an average of 15 minutes).
Each member of the team has to answer three important questions
- What he/she did yesterday?
- What he/she will do today?
- The problem he/she is facing . . . He/she blocked due to. . .
H1Definition of Done
Agile Definition of done is defined into three different stages called User Story (Requirement), Iteration, and product Release. These are given below:
H1Product Backlog
The agile product backlog in Scrum is a list of prioritized features. It contains a short description of all the functionalities desired in the product. In usual scenario, items should be broken down into user stories. Commonly, a Scrum team and its product owner write everything that they can think for agile backlog prioritization.
Product Backlog includes:
- Features
- Bugs
- Technical work
- Knowledge acquisition
H2Why Product Backlog is Important?
- The backlog is prepared to provide an estimate of each feature.
- It helps in the planning of the product's roadmap.
- It helps in re-ranking the features of the product by adding more value to it.
- It assists in determining the priority of the product first. The team member works first on the higher priority product.